In an era where transparency, environmental responsibility, and social governance define corporate success, sustainability reporting has emerged as a pivotal tool for businesses. It transcends mere compliance, embedding itself into the core of strategic corporate positioning, brand reputation enhancement, and stakeholder engagement.
The Strategic Value of Sustainability Reporting
Sustainability reporting provides a structured methodology for disclosing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives and their outcomes. It’s a practice that signals to investors, consumers, and regulatory bodies that a company is committed not only to profit but also to the planet and its people.
Visuals: Infographics Highlighting Key Benefits
- Brand Enhancement: Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability can significantly elevate a brand’s value, fostering loyalty among environmentally conscious consumers.
- Investor Attraction: Sustainability reporting can attract investors looking for long-term, sustainable investments, showcasing a company’s dedication to mitigating risks associated with climate change and social inequities.
- Regulatory Compliance: With the global shift towards mandatory ESG disclosures, effective sustainability reporting ensures compliance, avoiding potential fines and sanctions.
The Components of Effective Sustainability Reporting
Effective sustainability reporting is characterized by:
- Transparency: Offering an honest, clear view into the company’s sustainability efforts, successes, and areas for improvement.
- Accountability: Holding the company responsible for its impact on the environment and society.
- Engagement: Creating a dialogue with stakeholders to gather insights and inform future strategies.
Visuals: Step-by-Step Process Diagram
A detailed diagram outlining the process of sustainability reporting, from data collection and analysis to stakeholder engagement and report publication.
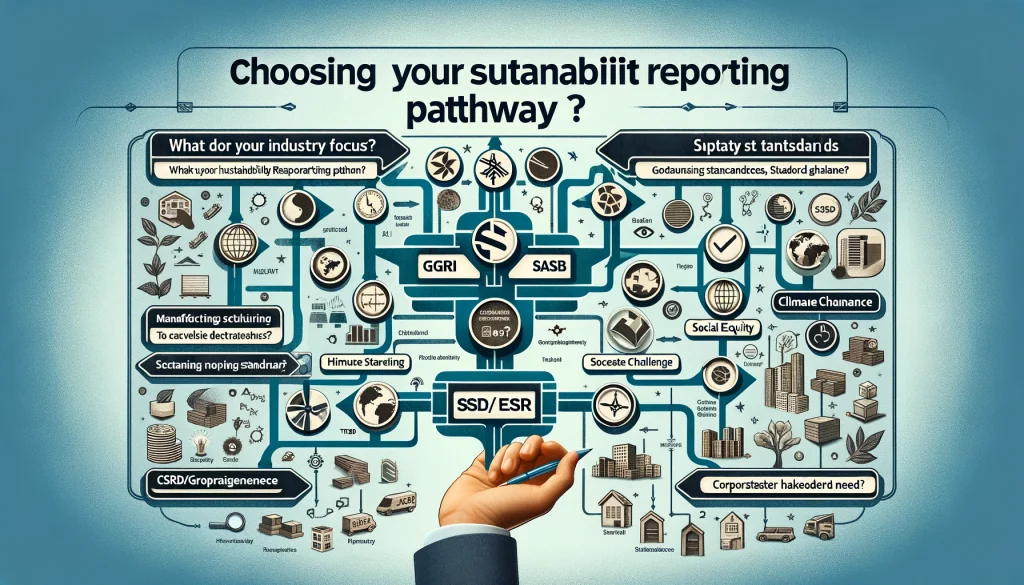
Aligning with Global Standards
Sustainability reporting is not a one-size-fits-all process. It requires alignment with global standards such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and the upcoming Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) in the EU.
Visuals: Decision Trees
Decision trees to help companies identify which reporting standards are most relevant to their operations and stakeholder needs.
Key Takeaway
In the landscape of modern business, sustainability reporting is not optional—it’s a strategic imperative. It enhances brand value, ensures compliance, and positions companies as leaders in corporate responsibility. For board members, CFOs, and sustainability officers, embracing sustainability reporting is a step towards securing a company’s place in a future where sustainability is at the forefront of business success.